Uterine Fibroids
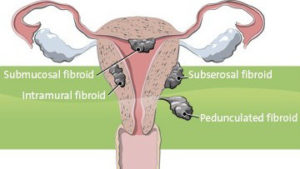
Uterine Fibroids are benign growths, (tumors) which originate from the muscular layer of the uterus. They develop from the smooth muscular tissue of the uterus. Upon hormonal stimulation, uterus muscle (myometrium) can growth fast, leading to creation of a mass called a fibroid. The growth patterns of uterine fibroids vary — they may grow slowly or rapidly. In postmenopausal women, many fibroid tumors tend to shrink secondary to a significantly lower hormonal level.
Fibroids can range in size from fraction of an inch, to bulky masses. They can be single or multiple, at times expanding the size of the uterus above the umbilicus.
Depending on the ethnic background, the prevalence of uterine fibroids varies form 50-85% . They can by asymptomatic or associated with multiple symptoms such as heavy vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, back pain, frequent urination, or constipation.
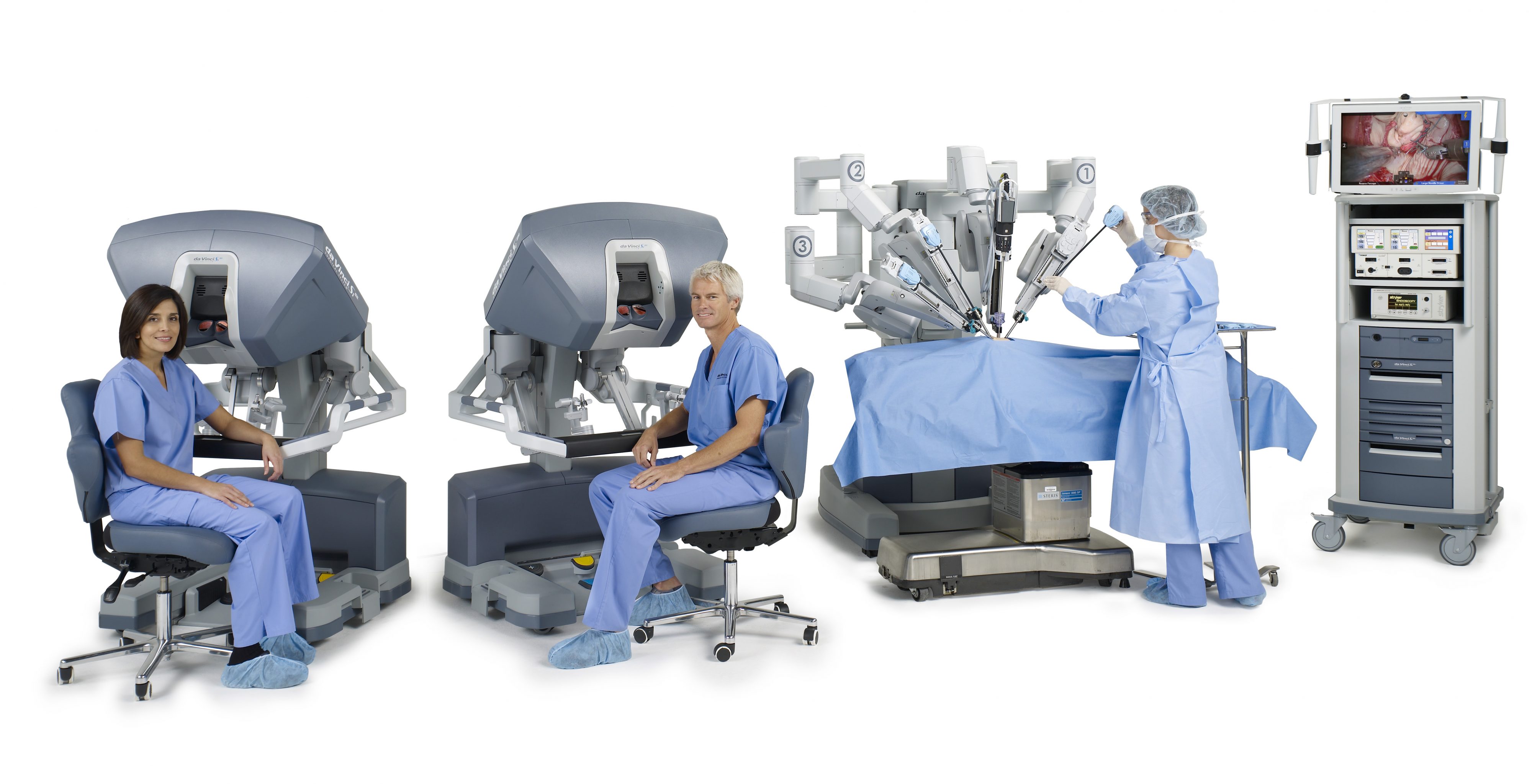
There are many treatment options available depending on their size, location, number, and symptoms perceived. One of the most advanced treatment options include the daVinci platform, which enables a very precise and safe surgical option.
Uterine Fibroids Symptoms
The following are the most common symptoms of uterine fibroids:
-
Prolonged menstrual periods
-
Heavy menstrual bleeding
-
Pelvic pain
-
Back pain
-
Frequent urination
-
Difficulty emptying your bladder
-
Constipation
-
Leg pain associated with difficult ambulation
Tests and Diagnosis
Once there is a clinical suspicion for uterine fibroids, the following test may be performed:
-
Ultrasound- If confirmation is needed, an ultrasound may be performed to determine the number and size of uterine fibroids.
-
Lab tests- in case of heavy vaginal bleeding, blood test is obtained to determine if there is any evidence of anemia.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)- is usually ordered if conventional ultrasound is not adequate or before surgical management of uterine fibroids, myomectomy. The test is able to provide an accurate assessment of the number, size and location of fibroid tumors within the uterus.
-
Sonohysterography- also called a saline infusion sonogram, uses sterile saline to expand the uterine cavity, enabling a more accurate evaluation of uterine cavity and endometrium.
-
Hysteroscopy- ror this, test, a small, lighted telescope called a hysteroscope is inserted through your cervix into your uterus. Saline is infused into your uterus, expanding the uterine cavity and allowing visualization of the walls of your uterus and the openings of your fallopian tubes.
Treatment
Treatment Options for Fibroids:
Medical:
1. Hormonal Management ( GNRH Agonists)
2.IUD MIRENA ( Progestin Releasing Intrauterine Devise)
3. Other Medication ( Birth Control Pills)
Minimally Invasive Procedures:
1. Uterine artery embolization (Procedure which consists of blockage of blood vessels supplying uterine myomas)
2. Accessa (This methods includes destruction of fibroids using an ultrasonic energy).
Minimally Invasive Surgery:
- 1. DaVinci/Laparoscopic Myomectomy
- 2. daVinci/Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
- 3. Hysteroscopic Myomectomy
Open Procedures:
3. Open Hysterectomy
4. Open Myomectomy